METAL CLAD PCB'S
— SUPERIOR THERMAL EFFICIENCY —
ABOUT METAL CLAD PCBS
MCPCB (Metal Clad Printed Circuit Board) technology was initially designed in the 60’s for high power applications. Known also as MPCB (Metal Printed Circuit Boards) or IMS (Insulated Metal Substrate). Since then it has been used widely in the LED industry, where the benefits of reduced junction temperatures have been realised.
With the boom of the LED lighting industry in the last 10 years, the demand for metal clad PCBs has risen dramatically. Metal circuit technology is now being used in all sorts of applications ranging from industrial to automotive. With this we have seen an influx of material providers influencing the market with new technology. From the 2-3 material providers years ago to the many we see on the market today.
The advantage of using metal clad material for PCB production as opposed to more traditional materials such as FR4 and CEM is simply to do with the efficient removal of heat. The dielectric insulating material in metal clad materials is designed to have a much superior thermal conductivity than that of FR4—generally ranging from 1W/m-K to 9W/m-K. Allowing for efficient heat removal.
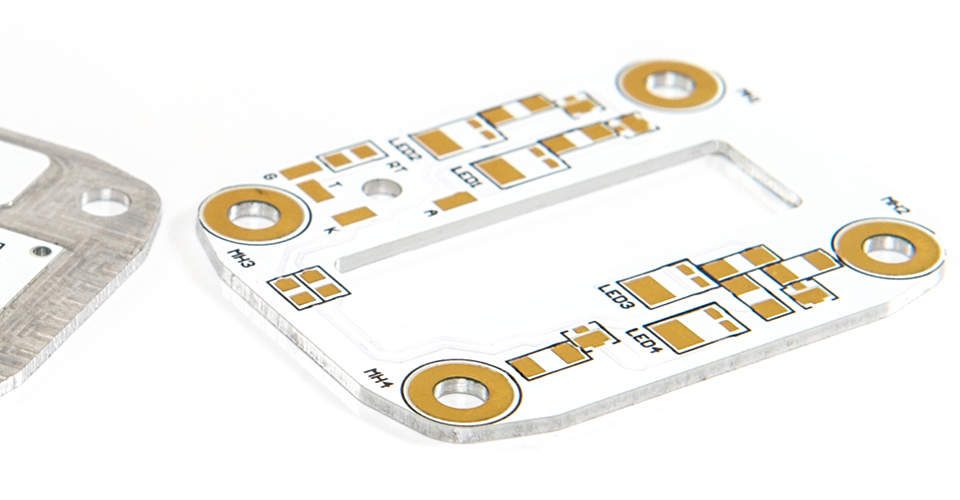
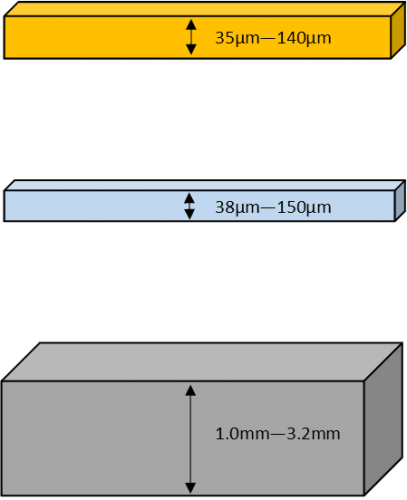
The material used to fabricate metal clad PCBs is made of 3 parts; The base layer, the dielectric, and the copper foil –
THE COPPER FOIL
This is the top copper layer of the material that will eventually be processed into the electrical conductors as per conventional PCBs. Generally 1oz-4oz but can be greater.
THE DIELECTRIC
This is the key part. This is the substance that both electrically isolates the Aluminium base layer from the copper foil, but also allows for rapid heat transfer between the two. It ensures that the heat generated in the components is dispersed to the heat sink as quickly as possible and determines the materials thermal properties. This is the ingredient of the substrate that sets apart a world class material from the cheaper alternatives on the market.
THE BASE LAYER
In the vast majority of cases the base layer is aluminium, generally 1mm-3.2mm thick (most commonly 1.6mm). Aluminium is a very efficient conductor of heat and as such is perfect for applications involving rapid heat transfer.